
Focal
What happens during a focal seizure varies as there are a wide range of symptoms.
You might hear people calling focal seizures by their old name: partial seizures.
Fast facts
-
1There are 2 main types of focal seizure: focal aware and focal impaired awareness
-
2A wide range of symptoms can happen during a focal seizure. Some people have only one symptom while others experience several
-
3The part of brain the seizure affects has an impact on what happens during a focal seizure
-
4During a focal aware seizure, the person remains aware of what’s happening around them
-
5If the person is not aware of what’s happening at any time during the seizure, it’s a focal impaired awareness seizure
-
6Focal aware seizures used to be called simple partial seizures
-
7Focal impaired awareness seizures used to be called complex partial seizures
What happens
What you experience, and what people will see, during a focal seizure depends on which part of the brain is affected. This is because different parts of the brain control our movements, body functions, feelings and reactions.
-
Focal aware seizures
Most focal aware seizures tend to be brief and will often only last a few seconds. Sometimes they are longer and can last for a couple of minutes. During a focal aware seizure, you remain aware.
You could experience a range of symptoms, such as:
- Unusual body movements, such as stretching one arm while the other bends
- A rising feeling in the stomach – like the sensation of being on a rollercoaster
- Feeling like what’s happening has happened before (déjà vu)
- Seeing flashing lights, colours or patterns
- Experiencing an unpleasant taste or smell
- Prickling, crawling or electric shock sensations, which may spread along the part of the body affected
- Seeing things as larger or smaller than they really are, or seeing things that aren’t there
- Feeling like all or part of your body is moving or floating
People sometimes call these seizures ‘warnings’ or ‘auras’ because they can be a sign that another type of seizure is about to happen. The symptoms may not be obvious to other people.
-
Focal impaired awareness seizures
Focal impaired awareness seizures tend to last longer, typically between 1 and 2 minutes. During a focal impaired awareness seizure, you may have some awareness, or you may lose awareness completely. You may not be able to respond to people during the seizure. And you may have no memory of it afterwards.
There are a range of symptoms, such as:
- Automatic behaviours such as fidgeting, undressing or plucking at clothes
- Lip smacking, repeated swallowing or chewing
- Kicking, pedalling, thrashing or rocking movements
- Screaming, swearing or laughing
- Your head or eyes turning to one side
- Changes to your skin tone or heart rate
These seizures can look like random actions or movements to other people.
The lobes in your brain
Focal seizures can start in different parts of the brain, and create a range of symptoms. Click or tap the markers to find out more.
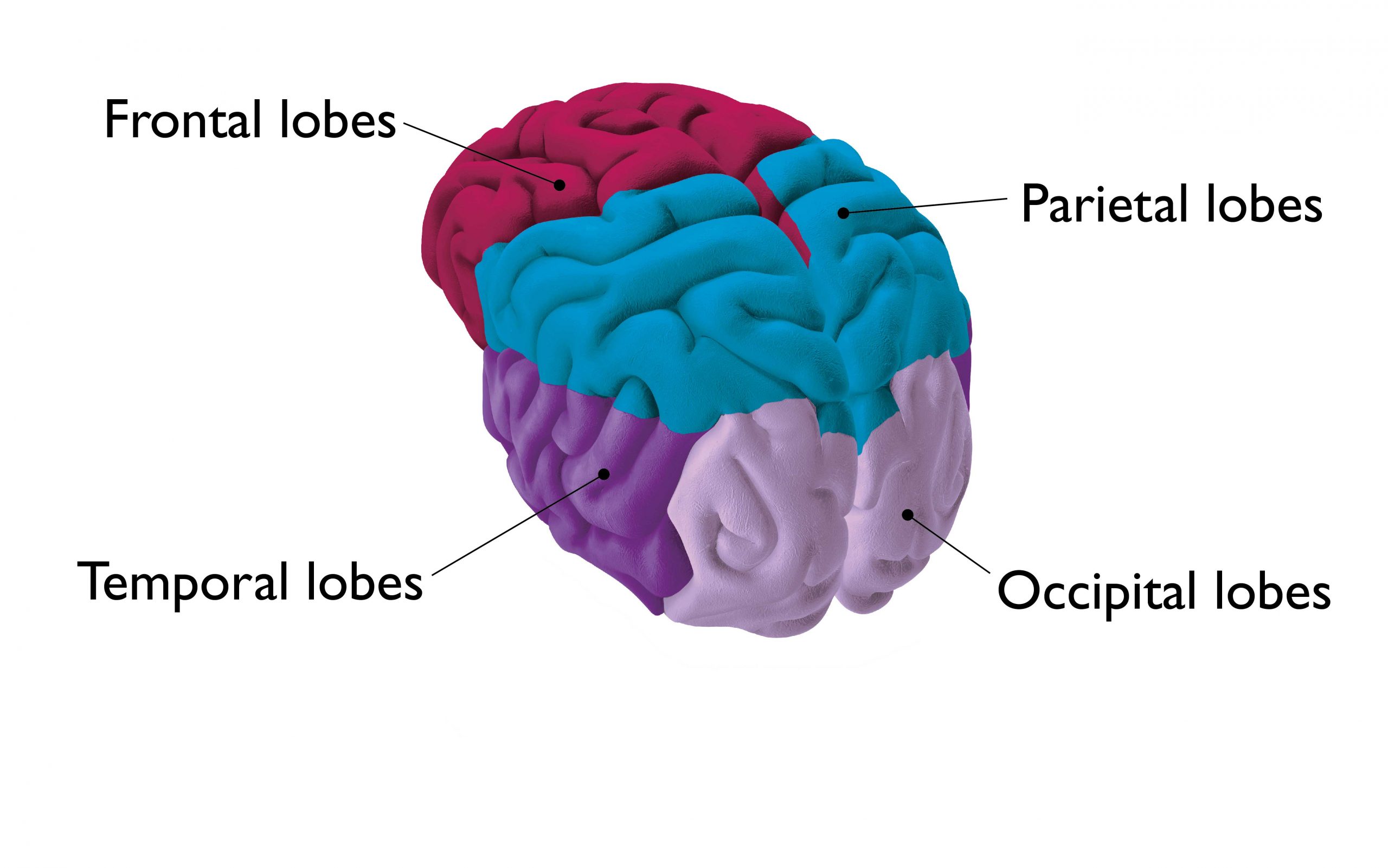
Frontal lobes
Focal seizures starting in the frontal lobes are common. The frontal lobes are responsible for many functions such as: personality, behaviour, movement, concentration and problem solving.
Parietal lobes
Seizures starting in the parietal lobe often spread to involve other lobes. The parietal lobes are responsible for: processing language, signals from our senses and spatial awareness.
Temporal lobes
Focal seizures starting in the temporal lobes are common. The temporal lobes are responsible for many functions, such as hearing, speech, memory, and emotions.
Occipital lobes
Seizures starting in the occipital lobes often spread to involve other lobes. The occipital lobes are responsible for vision.
How people can help
If you have focal seizures
It’s helpful for others to:
- Know that focal seizures can be frightening and disorientating
- Time the seizure
- Stay with you and ensure you are safe
- Guide you away from danger
- Be calm and reassuring
- Know that medical help isn’t usually needed, but if there are any serious injuries seeking first aid or getting medical help might be necessary
- Check how you’re feeling afterwards and explain anything you might have missed
- Call an ambulance if the seizure lasts for more than 5 minutes
It’s not helpful to:
- Crowd you
- Restrain you
- Try to bring you round – it’s not possible
- Put anything in your mouth
- Give you any food or drink, until you have fully recovered
After the seizure
How people feel after a focal seizure varies.
You might feel fine and be able to get back to what you were doing straight away. Or you could feel confused or tired for some time afterwards. You may want to sleep afterwards to help you recover.
Sometimes people experience a temporary weakness or can’t move part of their body after a seizure. This is called Todd’s paresis or Todd’s paralysis. It can last from a few minutes to a few days before going away.

Watch
Different experiences of focal seizures
Do something
Keeping a seizure diary really helps people to understand their seizures better.
What percentage of your seizures are you recording in a seizure diary?
Go to the Seizures menu







